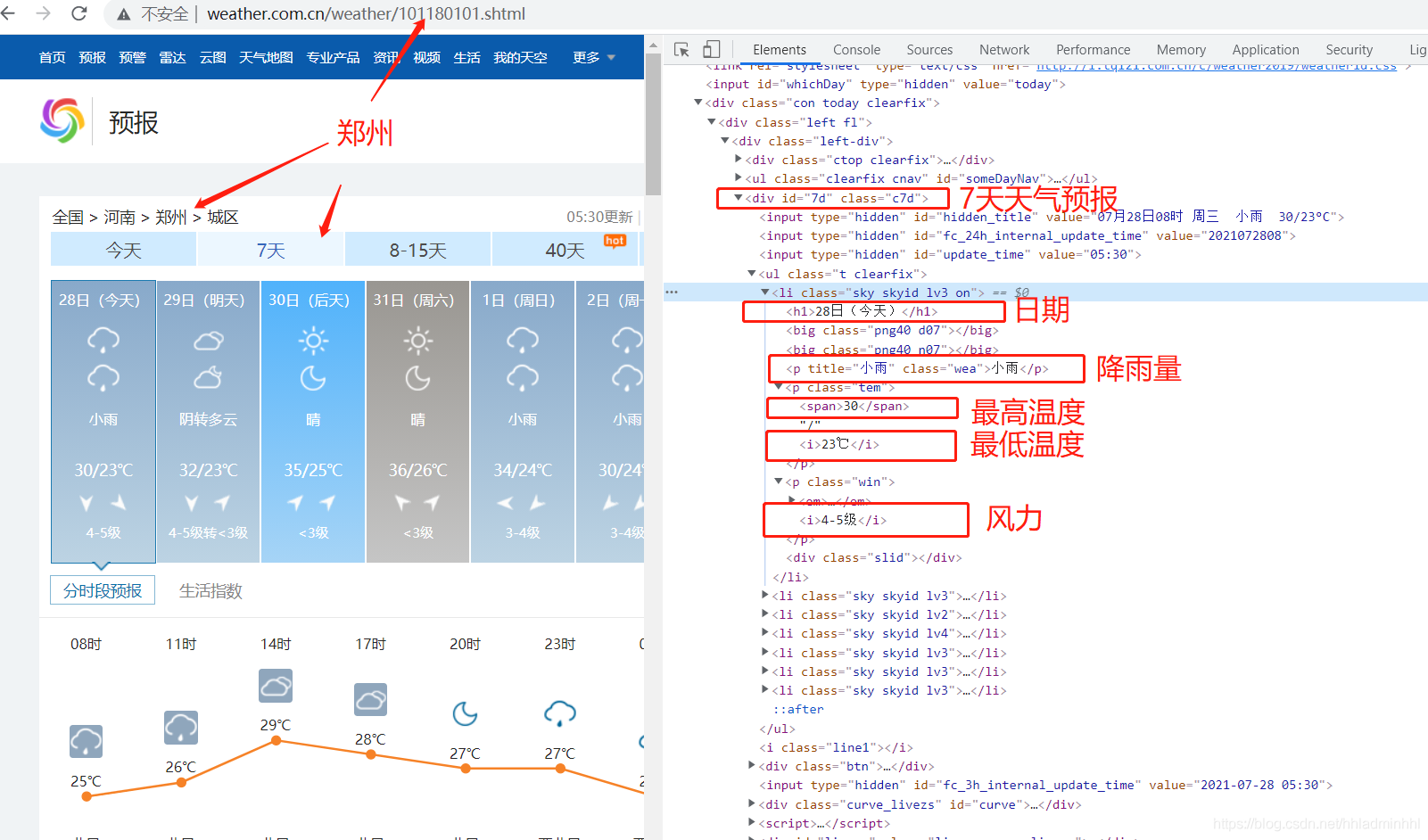
Citycode = { "郑州": "101180101",
"新乡": "101180301",
"许昌": "101180401",
"平顶山": "101180501",
"信阳": "101180601",
"南阳": "101180701",
"开封": "101180801",
"洛阳": "101180901",
"商丘": "101181001",
"焦作": "101181101",
"鹤壁": "101181201",
"濮阳": "101181301",
"周口": "101181401",
"漯河": "101181501",
"驻马店": "101181601",
"三门峡": "101181701",
"济源": "101181801",
"安阳": "101180201"}
citycode_lists = list(Citycode.items())
for city_code in citycode_lists:
city_code = list(city_code)
print(city_code)
citycode = city_code[1]
cityname = city_code[0]
url1 = 'http://www.weather.com.cn/weather/'+citycode+ '.shtml'
html1 = getHTMLtext(url1)
data1, data1_7 = get_content(html1,cityname)
存储数据:
def write_to_csv(file_name, data, day=14):
"""保存为csv文件"""
with open(file_name, 'a', errors='ignore', newline='') as f:
if day == 14:
header = ['日期','城市','天气','最低气温','最高气温','风向1','风向2','风级']
else:
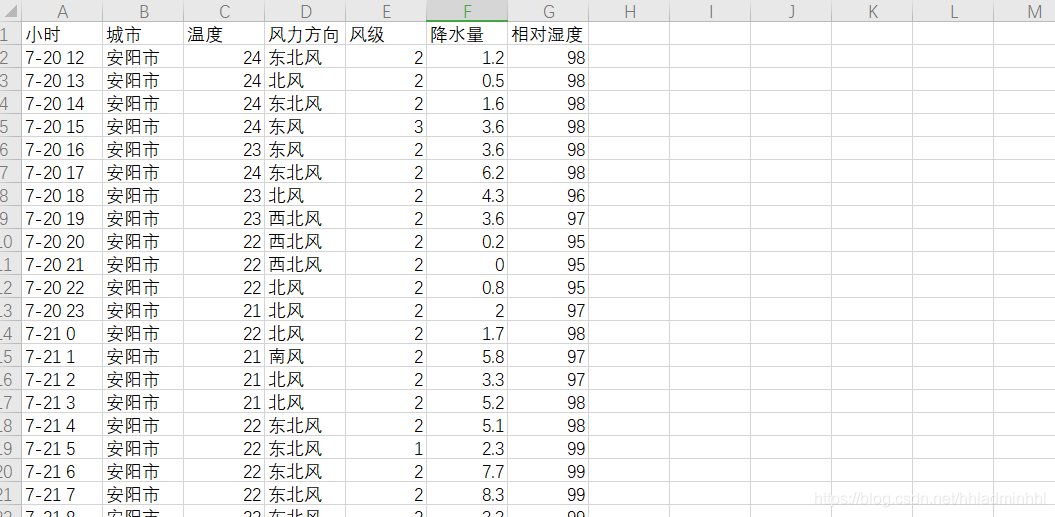
header = ['小时','城市','温度','风力方向','风级','降水量','相对湿度','空气质量']
f_csv = csv.writer(f)
f_csv.writerow(header)
f_csv.writerows(data)
write_to_csv('河南天气.csv',data_all,1)
这样我们就可以把全省的各个地级市天气数据保存下来了。
2. 风向风级雷达图
统计全省的风力和风向,因为风力风向使用极坐标的方式展现比较清晰,所以我们采用极坐标的方式展现一天的风力风向图,将圆分为8份,每一份代表一个风向,半径代表平均风力,并且随着风级增高,蓝色加深。
def wind_radar(data):
"""风向雷达图"""
wind = list(data['风力方向'])
wind_speed = list(data['风级'])
for i in range(0,24