# 调用
from protobuf_to_dict import protobuf_to_dict
b = b'\n\x07request\x10\x01\x1a\x15\n\x0fhello protobuf!\x12\x02mk \x02*\x02\x01\x022\x0c\n\x03abc\x12\x05world2\x0c\n\x03efg\x12\x05world2\n\n\x011\x12\x05world2\n\n\x012\x12\x05world:\x02\x00\x01'
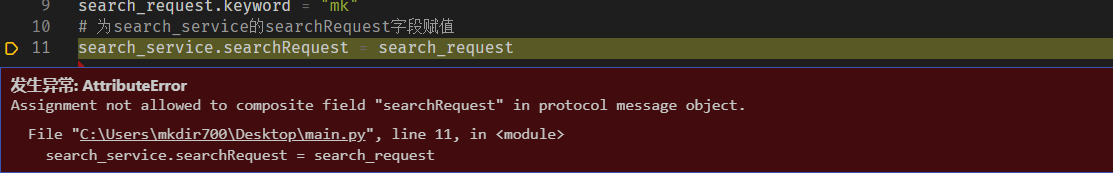
search_service.ParseFromString(b)
# print(search_service.type)
d = protobuf_to_dict(search_service)
print(d, type(d))
# {'type': 'request', 'id': 1, 'searchRequest': {'content': 'hello protobuf!', 'keyword': 'mk'}, 'searchType': 2, 'uid': [1, 2], 'seconds': [{'type': 'abc', 'word': 'world'}, {'type': 'efg', 'word': 'world'}, {'type': '1', 'word': 'world'}, {'type': '2', 'word': 'world'}], 'sortOrder': [0, 1]} <class 'dict'>
小小尝试
本文中例子,我做了一个接口。
接口地址: http://47.101.154.110:8000/
| 请求头 |
请求体 |
请求方式 |
| 必须指定Content-Type: application/grpc-web+proto |
序列化后的二进制 |
POST |
你可以使用postman提交数据,来查看结果
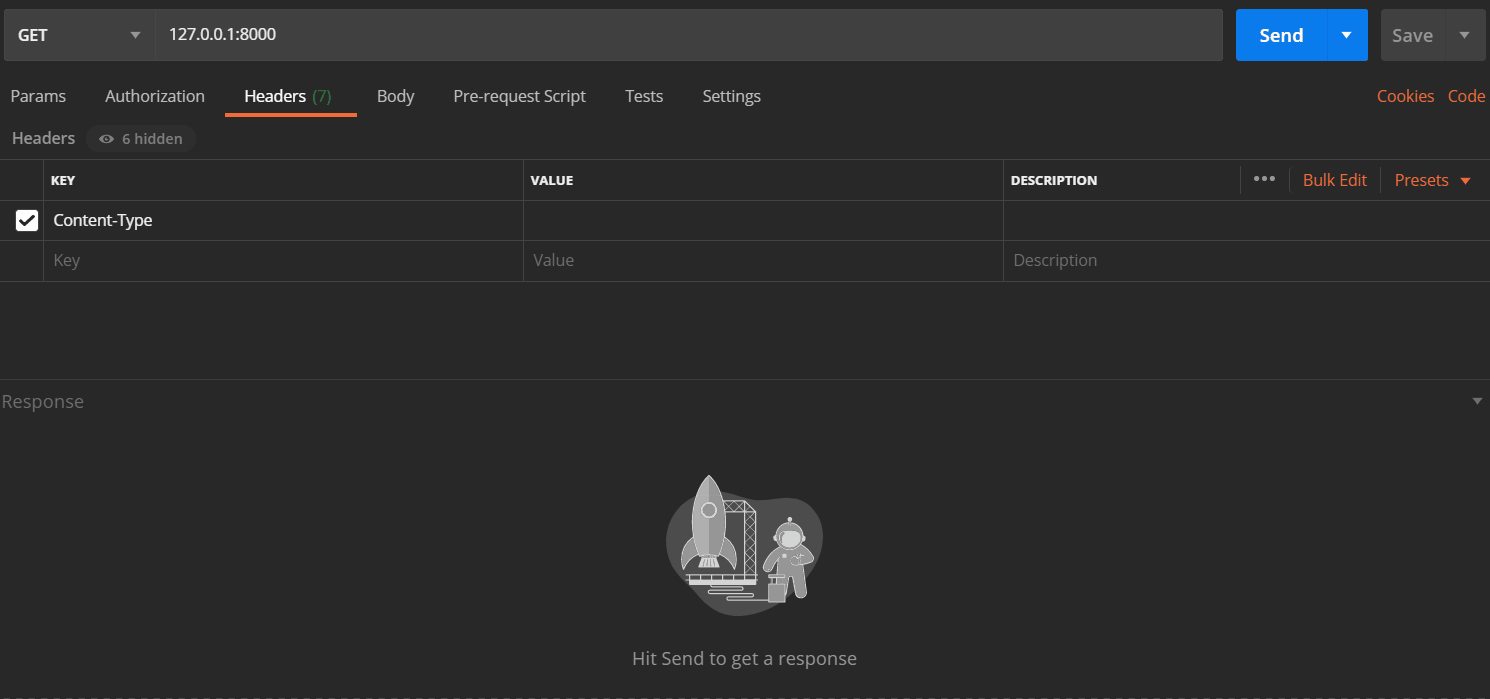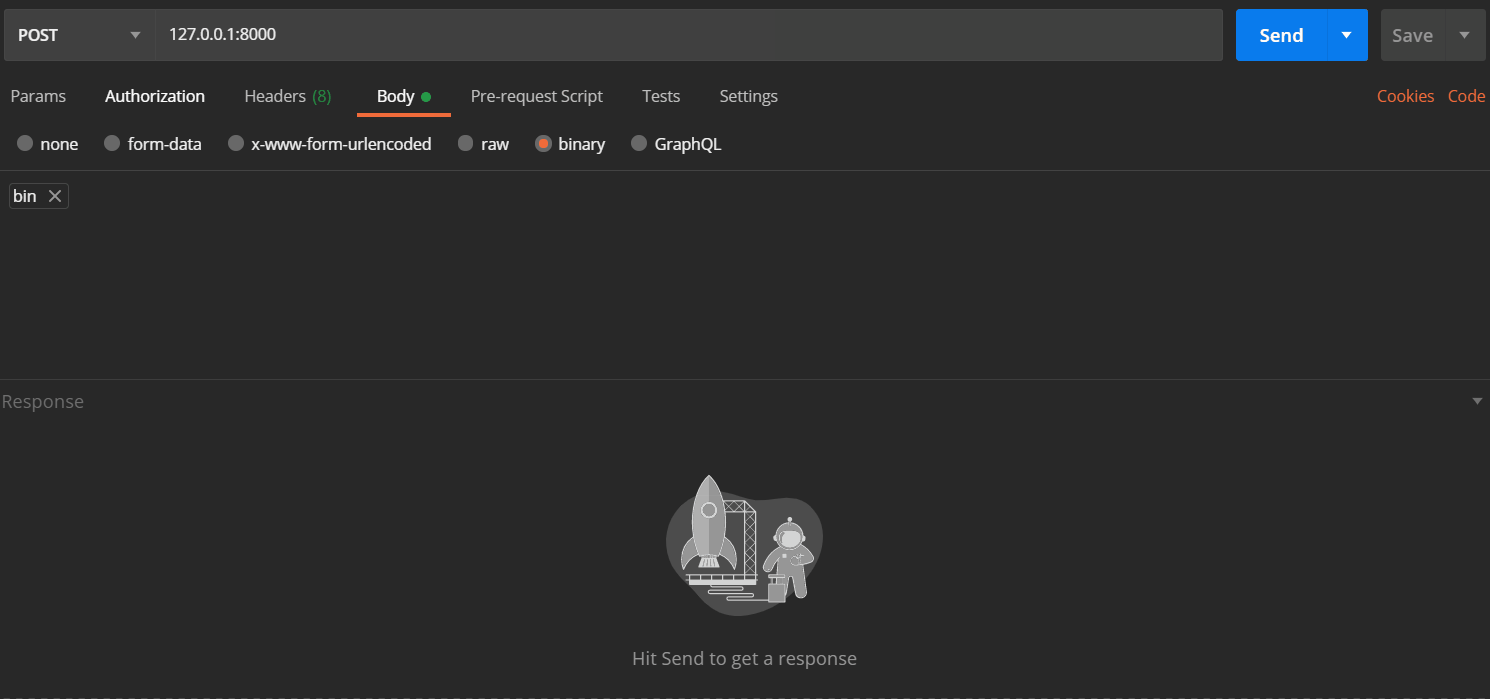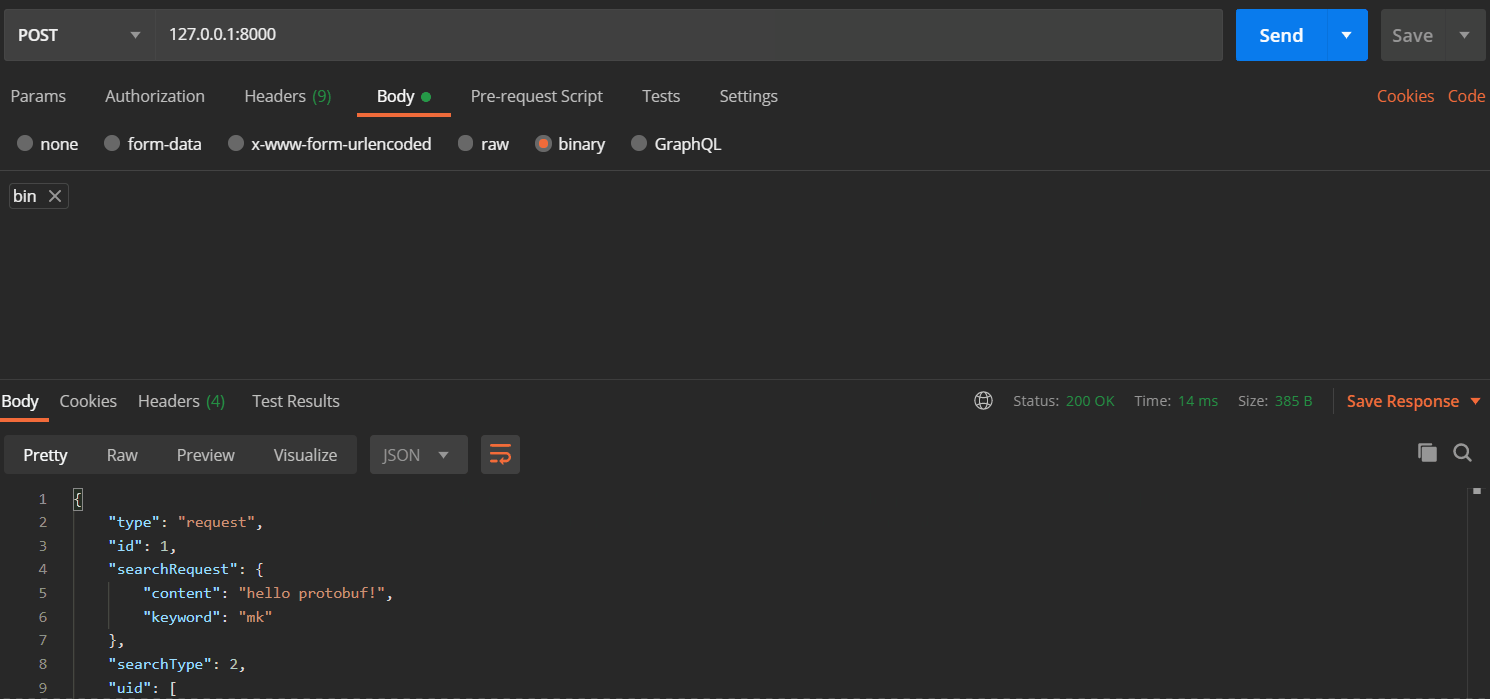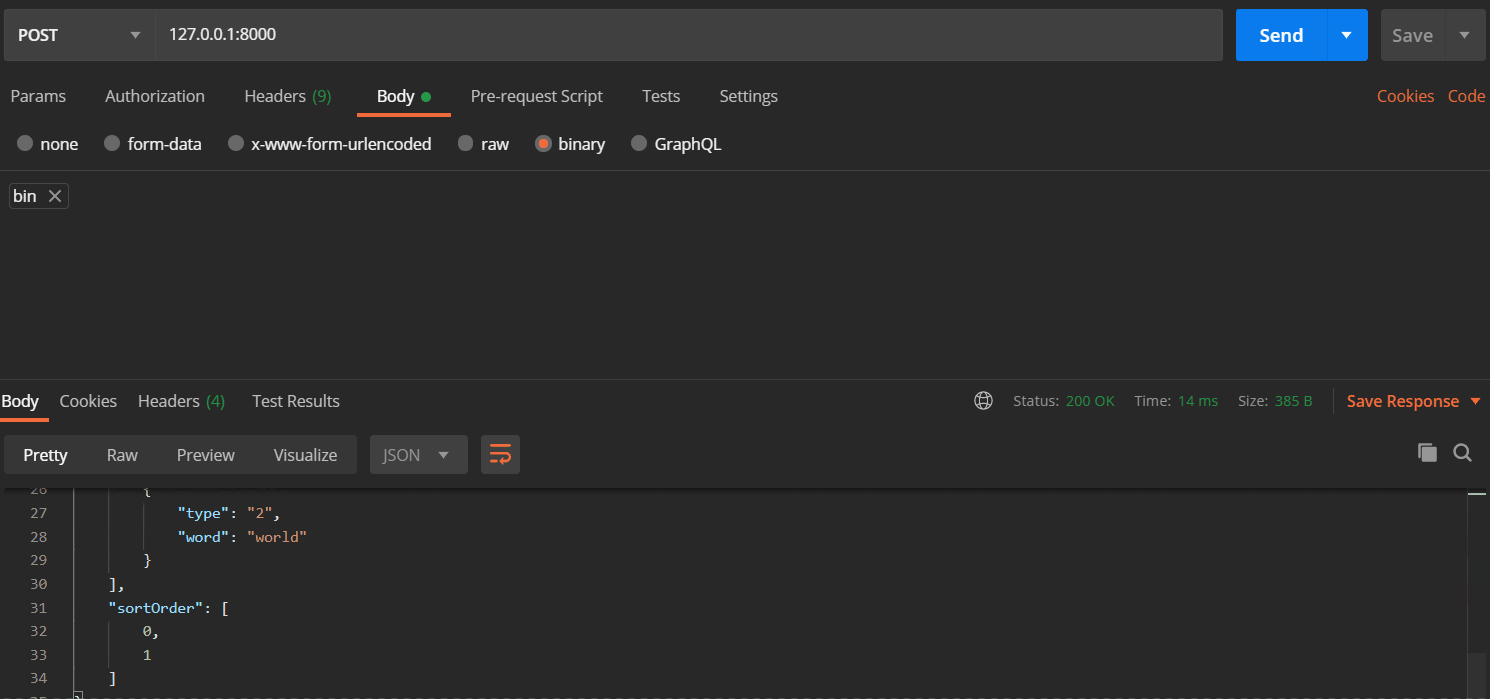
也可以使用Python发送请求
import requests
headers = {
'Content-Type': 'application/grpc-web+proto'
}
b = b'\n\x07request\x10\x01\x1a\x15\n\x0fhello protobuf!\x12\x02mk \x02*\x02\x01\x022\x0c\n\x03abc\x12\x05world2\x0c\n\x03efg\x12\x05world2\n\n\x011\x12\x05world2\n\n\x012\x12\x05world:\x02\x00\x01'
resp = requests.post('http://47.101.154.110:8000/', data=b, headers=headers)
print(resp.text)
完整的test.proto
syntax = "proto3";
message SearchService {
string type = 1;
int32 id = 2;
// 定义一个message类型
message SearchRequest {
string content = 1;
string keyword = 2;
}
// 类型 字段名 序号
SearchRequest searchRequest = 3;
enum SearchType {
A = 0;
B = 1;
}
SearchType searchType = 4;
repeated int32 uid = 5;
message Second {
string type = 1;
string word = 2;
}
repeated Second seconds = 6;
enum SortOrder {
key1 = 0;
key2 = 1;
key3 = 2;
}
repeated SortOrder sortOrder = 7;
}
完整的赋值示例
import test_pb2 as pb
from protobuf_to_dict import protobuf_to_dict
search_service = pb.SearchService()
search_service.type = "request"
search_service.id = 1
search_service.searchRequest.content = "hello protobuf!"
search_service.searchRequest.keyword = "mk"
# search_service.searchType = pb.SearchService.SearchType.A
search_service.searchType = 2
search_service.uid.append(1)
search_service.uid.append(2)
second = search_service.Second()
second.type = 'abc'
second.word = 'world'
search_service.seconds.append(second)
search_service.seconds.append(search_service.Second(type='efg', word="world"))
seconds = [
search_service.Second(type='1', word="world"),
search_service.Second(type='2', word="world")
]
search_service.seconds.extend(seconds)
sortFields = [
search_service.SortOrder.key1,
search_service.SortOrder.key2
]
search_service.sortOrder.extend(sortFields)
b = search_service.SerializeToString()
print(b)
推荐模块
在使用编译包时,没有代码提示,还有点不习惯。
这里,推荐安装mypy-protobuf
pip install mypy-protobuf
使用方法:
在你使用protoc命令编译proto文件时,新增一个参数mypy-out=,就像这样
protoc --python_out=. --mypy-out=. test.proto
此时会生成两个文件,并将他们拖入项目中的同一目录
test_pb2.py:我们需要导入使用的编译包
test_pb2.pyi:存根文件,在编辑器中会有代码提示(想了解存根文件,可以看最下面的参考文章)
效果演示:

参考文章
https://github.com/dropbox/mypy-protobuf
pyi文件是干嘛的?(一文读懂Python的存根文件和类型检查)

 此文主要是总结,python使用protobuf的过程,如何序列化和反序列化,对不同类型的字段如何进行赋值。
此文主要是总结,python使用protobuf的过程,如何序列化和反序列化,对不同类型的字段如何进行赋值。